A Look at Standard Cathode Powders Used in SOFCs
Lanthanum Strontium Manganite (20%)
LSM20
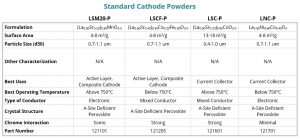
 Lanthanum strontium manganite is one of the most well characterized standard cathode powders for solid oxide fuel cells having zirconia based electrolytes . LSM typically works best at operating temperatures of 750 °C and higher, and has been a proven cathode in the SOFC industry for many years. Our LSM powder is prepared with a slight A-site deficiency to prevent adverse chemical reactions with zirconia. Our LSM cathode material can be applied by screen printing, painting or spraying after it is formulated into appropriate inks or suspensions. This LSM powder also can be mixed with one of our ceria-based electrolyte (GDC or SDC) or zirconia based electrolyte (YSZ or ScSZ) powders to improve cathode performance.
Lanthanum strontium manganite is one of the most well characterized standard cathode powders for solid oxide fuel cells having zirconia based electrolytes . LSM typically works best at operating temperatures of 750 °C and higher, and has been a proven cathode in the SOFC industry for many years. Our LSM powder is prepared with a slight A-site deficiency to prevent adverse chemical reactions with zirconia. Our LSM cathode material can be applied by screen printing, painting or spraying after it is formulated into appropriate inks or suspensions. This LSM powder also can be mixed with one of our ceria-based electrolyte (GDC or SDC) or zirconia based electrolyte (YSZ or ScSZ) powders to improve cathode performance.
View the Lanthanum Strontium Manganite (LSM20) Product Page
Lanthanum Strontium Cobalt Ferrite
LSCF
 Lanthanum strontium cobalt ferrite (LSCF) is one of the two primary standard cathode powders used by SOFC developers and manufacturers (LSM being the other). LSCF offers good performance at operating temperatures of 750 °C and lower, which makes it a quality option for use with anode supported SOFCs. Our LSCF powder is prepared with a slight A-site deficiency to improve its stability. LSCF can be used with zirconia (YSZ and ScSZ) ceria (GDC and SDC) and lanthanum gallate based electrolytes. A ceria barrier layer is recommended when using LSCF cathodes with zirconia based electrolytes. Our LSCF cathode material can be applied by screen printing, painting or spraying after it is formulated into appropriate inks or suspensions. LSCF also can be mixed with one of our ceria-based electrolyte (GDC or SDC) to improve cathode performance.
Lanthanum strontium cobalt ferrite (LSCF) is one of the two primary standard cathode powders used by SOFC developers and manufacturers (LSM being the other). LSCF offers good performance at operating temperatures of 750 °C and lower, which makes it a quality option for use with anode supported SOFCs. Our LSCF powder is prepared with a slight A-site deficiency to improve its stability. LSCF can be used with zirconia (YSZ and ScSZ) ceria (GDC and SDC) and lanthanum gallate based electrolytes. A ceria barrier layer is recommended when using LSCF cathodes with zirconia based electrolytes. Our LSCF cathode material can be applied by screen printing, painting or spraying after it is formulated into appropriate inks or suspensions. LSCF also can be mixed with one of our ceria-based electrolyte (GDC or SDC) to improve cathode performance.
View the Lanthanum Strontium Cobalt Ferrite (LSCF) Product Page
Lanthanum Nickel Cobaltite
LNC
 Lanthanum nickel cobaltite (LNC) is a high conductivity material that typically is used as a cathode contact paste (to improve cathode current collection) in SOFC stacks. LNC also can be used for the same purpose in single-cell SOFC testing. Compared to lanthanum strontium cobaltite, LNC has better thermal stability, lower thermal expansion and equivalent electrical conductivity. LNC also can be considered as a cathode material, when mixed with one of our ceria-based electrolyte powders (GDC or SDC).
Lanthanum nickel cobaltite (LNC) is a high conductivity material that typically is used as a cathode contact paste (to improve cathode current collection) in SOFC stacks. LNC also can be used for the same purpose in single-cell SOFC testing. Compared to lanthanum strontium cobaltite, LNC has better thermal stability, lower thermal expansion and equivalent electrical conductivity. LNC also can be considered as a cathode material, when mixed with one of our ceria-based electrolyte powders (GDC or SDC).
Typical Uses:
- Ink fabrication for screen printing applications
- SOFC cathode fabrication for electrolyte and anode supported cells
- Low temperature applications
- Current conducting material for multilayer cathodes
View the Lanthanum Nickel Cobaltite (LNC) Product Page
Lanthanum Strontium Cobaltite
LSC
 Lanthanum Strontium Cobaltite (LSC) is a highly conductive perovskite material that is often used as a “contact paste” in SOFC systems, where it creates the bond between the cathode of the cell and the current collector (often a metal mesh or plate). Our LSC powder can be easily fabricated into an ink for painting or screen printing. LSC has a relatively low sintering temperature, so it is best used in SOFCs operating at less than about 750 °C. Another design consideration for using LSC is its relatively high thermal expansion coefficient, which leads to expansion mismatches at higher operating temperatures.
Lanthanum Strontium Cobaltite (LSC) is a highly conductive perovskite material that is often used as a “contact paste” in SOFC systems, where it creates the bond between the cathode of the cell and the current collector (often a metal mesh or plate). Our LSC powder can be easily fabricated into an ink for painting or screen printing. LSC has a relatively low sintering temperature, so it is best used in SOFCs operating at less than about 750 °C. Another design consideration for using LSC is its relatively high thermal expansion coefficient, which leads to expansion mismatches at higher operating temperatures.
View the Lanthanum Strontium Cobaltite (LSC) Product Page
